“Insect Apocalypse:” US Farmland 48 Times More Toxic To Insects Than 25 Years Ago

Animal Health & Blue Gold™ Grand Champion PME®
January 11, 2019
15% OFF & FREE SHIPPING!
October 21, 2020A new study shows how "insect apocalypse" is unfolding across America's farmland since neonicotinoid pesticides were introduced several decades ago.
Researchers found that farmland across the country is 48 times more toxic to insect life than 25 years ago, and neonicotinoid pesticides account for a large majority of the increase in toxicity.
Researchers found that farmland across the country is 48 times more toxic to insect life than 25 years ago, and neonicotinoid pesticides account for a large majority of the increase in toxicity.
"It is alarming that US agriculture has become so much more toxic to insect life in the past two decades," said Kendra Klein, Ph.D., study co-author and senior staff scientist at Friends of the Earth.
"We need to phase out neonicotinoid pesticides to protect bees and other insects that are critical to biodiversity and the farms that feed us."
"We need to phase out neonicotinoid pesticides to protect bees and other insects that are critical to biodiversity and the farms that feed us."
Published in the journal PLOS ONE on Tuesday, the new study is a complete assessment of pesticide usage on farmland in the US, is the first study in the world to quantify how dangerous fields have become for insects by providing YoY changes in toxicity levels of the soil.

The increased toxic load measured in the study could explain why insect populations are collapsing in the US.
Klein said neonicotinoids are more toxic for insects than traditional pesticides and are widely used by farmers. These dangerous chemicals can remain in the soil for months to years after one application.

The increased toxic load measured in the study could explain why insect populations are collapsing in the US.
Klein said neonicotinoids are more toxic for insects than traditional pesticides and are widely used by farmers. These dangerous chemicals can remain in the soil for months to years after one application.
"Congress must pass the Saving America's Pollinators Act to ban neonicotinoids," said Klein.
"In addition, we need to rapidly shift our food system away from dependence on harmful pesticides and toward organic farming methods that work with nature rather than against it."
"In addition, we need to rapidly shift our food system away from dependence on harmful pesticides and toward organic farming methods that work with nature rather than against it."
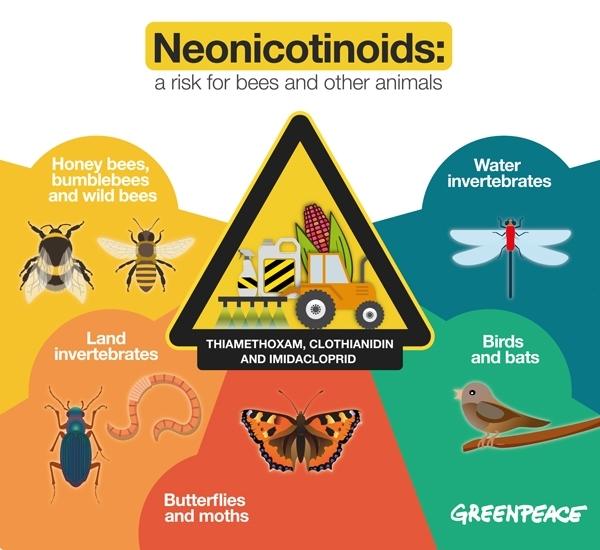
Photo by Greenpeace
The study suggests neonicotinoids are a major factor in the recent decline of insects, along with climate change and habitat destruction, leading scientist to warn of an "insect apocalypse."
Insects, such as honey bees, are the world's most important pollinator of food crops. It's estimated that at least one-third of food consumed by humans relies on pollination mainly by bees, but also by other insects, birds, and bats.
Neonicotinoid usage has been linked to honey-bee colony collapse disorder and loss of birds due to a decline in insect populations.
Klein said neonicotinoid became popular with farmers during the mid-2000s, has contributed to the dramatic increase of toxic farmland.
The study found imidacloprid and clothianidin, produced by Bayer, and thiamethoxam, a product of Syngenta-ChemChina were the three neonicotinoids that contributed to the increasing toxic load in farmlands.
Last year, Europe banned three main neonicotinoids (clothianidin, imidacloprid, and thiamethoxam) for all farming activity. Several states in the US have also restricted farmers from using the chemicals, out of fear that it could further collapse the honey bee population.
Neonicotinoid usage has been linked to honey-bee colony collapse disorder and loss of birds due to a decline in insect populations.
Klein said neonicotinoid became popular with farmers during the mid-2000s, has contributed to the dramatic increase of toxic farmland.
The study found imidacloprid and clothianidin, produced by Bayer, and thiamethoxam, a product of Syngenta-ChemChina were the three neonicotinoids that contributed to the increasing toxic load in farmlands.
Last year, Europe banned three main neonicotinoids (clothianidin, imidacloprid, and thiamethoxam) for all farming activity. Several states in the US have also restricted farmers from using the chemicals, out of fear that it could further collapse the honey bee population.
Read Tyler Durden's full article here.





